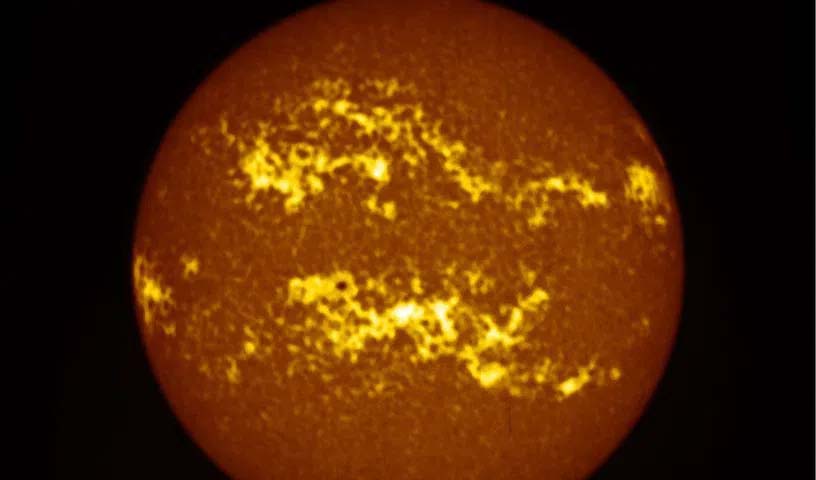
Bengaluru: Two onboard remote sensing instruments of ISRO’s Aditya-L1 spacecraft have captured the recent solar flare, the space agency said on Monday. India’s first solar mission Aditya-L1 reached the Lagrangian point (L1) on January 6 this year, 127 days after its launch on September 2, 2023. L1 is located about 1.5 million km from Earth and enables the spacecraft to observe the Sun continuously. The Solar Ultra Violet Imaging Telescope (SUIT) and Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC) have captured the dynamic activities of the Sun during May 2024, ISRO said in a statement.
“Several X-class and M-class flares associated with coronal mass ejections (CMEs), which lead to significant geomagnetic storms, were recorded,” it said. The active region AR13664 on the Sun, during its passage during the week of May 8-15, erupted several X-class and M-class flares, which were associated with CMEs during May 8 and 9. These generated a major geomagnetic storm on May 11, it was said. ISRO released images of the Sun obtained by the SUIT payload on May 17, and also shared details of the observations made by the VELC.